논문
- 시계열데이터 의료논문 요약 PPT 2022.10.13
- Novel Machine Learning Can Predict Acute Asthma Exacerbation 논문 리뷰 2021.04.27
- 천식 머신러닝 논문 리뷰 - Deep learning facilitates the diagnosis of adult asthma, Katsuyuki Tomita 2020.03.16
- Clinical and inflammatory characteristics of the European U-BIOPRED adult severe asthma cohort 2019.12.30
- 논문 abstract 간단 정리 - Omics 연구 영국 기관 논문 2019.12.27
시계열데이터 의료논문 요약 PPT
Novel Machine Learning Can Predict Acute Asthma Exacerbation 논문 리뷰
journal.chestnet.org/action/showPdf?pii=S0012-3692%2821%2900031-3
IF가 10점대의 저널 논문으로 좋은 예시라고 생각합니다.
목표: 천식 악화를 예측하는 머신러닝 모델을 수립
1. Baseline characteristics
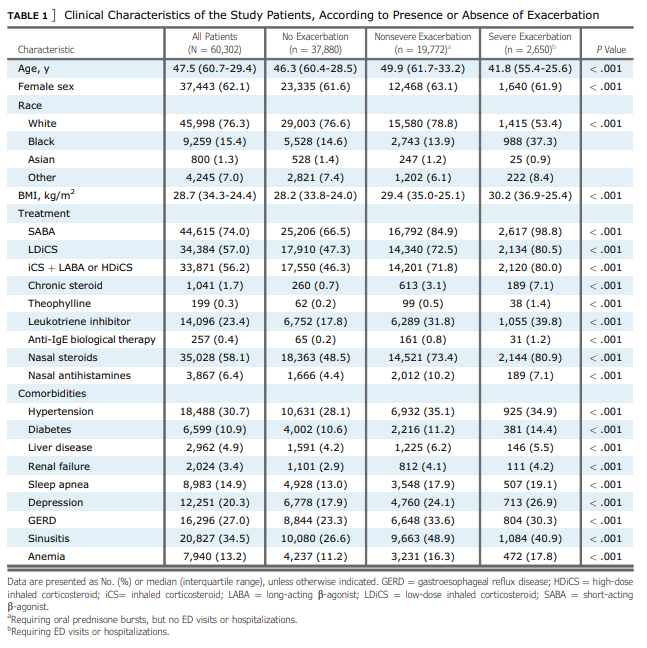
2. 천식악화 outcome 분류
- nonsevere asthma exacerbation : systemic steroid를 28일 이하로 사용한 환자
- ED : Emergency Room visit history
- hospitalization : Hospitalization visit history
3. 논문의 특징
- 약물 사용력을 포함( outcome에 직접적인 영향을 줄 수 있음에도 불구하고)
- NaN데이터를 살림 (n = 10만명)
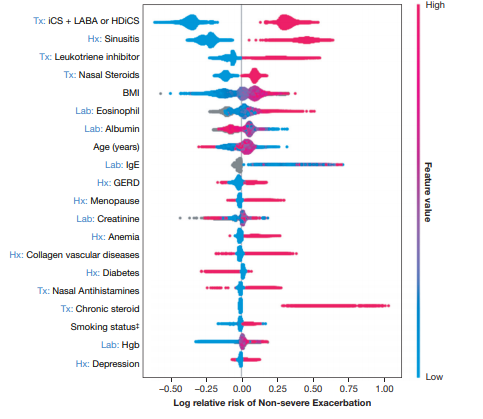
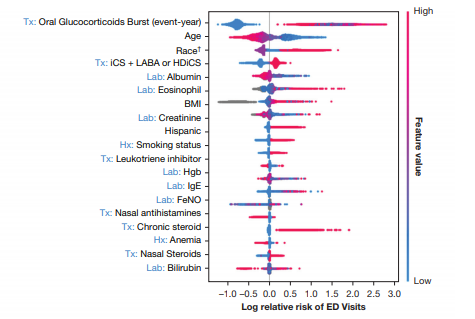
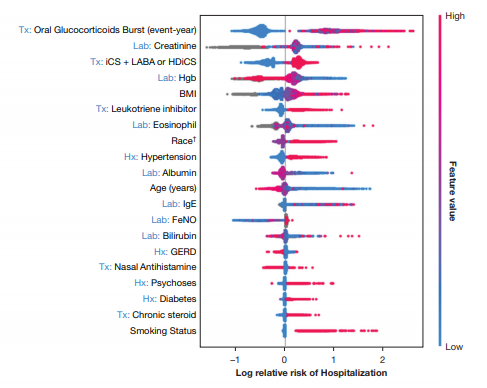
- SHAP로 각 feature의 importance를 설명하고, LightGBM모델로 성능을 최대로 끌어냄
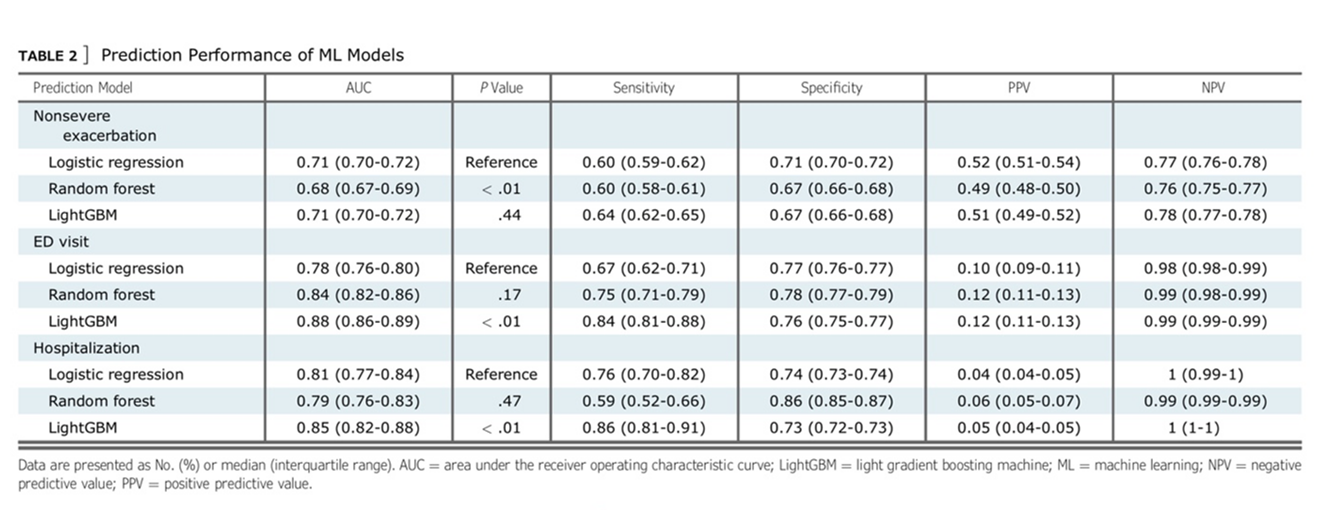
- AUC, recall, precision, PPV, NPV 제안
- 메인 feature는 이전에 약물조합(ICS, LABA), HDiCs, oral glucocorticoid burst history 등 그 후 race, age등. outcome의 종류에 따라 변함.
4. 사용모델
- Logistic regression
- Random forest
- Light GBM
5. Test data: 1만명의 replicative cohort를 사용하여 test.
6. 결론
- 약물정보가 1st risk factor.
- 만약, lung function test data가 들어간다면, FEV1, FVC, FEV1/FVC가 main feature가 되지만 모델 performance에 영향을 주지 않음
- Asthma exacerbation의 경우에는 LightGBM과 logistic regression model의 결과가 다르지 않으나, ED와 hospitalization에 대해서는 outperform
7. SHAP
'논문 > 의료논문' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 천식 머신러닝 논문 리뷰 - Deep learning facilitates the diagnosis of adult asthma, Katsuyuki Tomita (0) | 2020.03.16 |
|---|---|
| 논문 abstract 간단 정리 - Omics 연구 영국 기관 논문 (0) | 2019.12.27 |
천식 머신러닝 논문 리뷰 - Deep learning facilitates the diagnosis of adult asthma, Katsuyuki Tomita
Deep learning facilitates the diagnosis of adult asthma
We explored whether the use of deep learning to model combinations of symptom-physical signs and objective tests, such as lung function tests and the …
www.sciencedirect.com
Summary
Background: symptom-physical signs과 objective tests의 조화에 딥러닝을 적용하였을 때, 어른 천식환자들의 초기 진단을 예측하는데 머신러닝보다 더 나은 성능을 보였다.
Methods: Kindai 대학병원에 non-specific respiratory symptoms을 가지고 처음 방문한 566명의 환자의 후향적 데이터를 이용. logistic, SVM, DNN사용.
Results: symptom-physical sign만으로 모델을 돌리면 대략 DNN,SVM,logistic이 0.65정도의 acc를 갖는데, biochemical findings, lung function test, bronchial challenge test를 추가하여 모델을돌리면 DNN은 0.98의 높은 정확도를 보이고 SVM: 0.82, logistic은 0.94wjdeh.
Conclusions: classical machine learning에 비해 adult asthma를 진단하는데 매우 용이하다.
1. Introduction
외적인 기침, 숨쉬기 어려움, 쎅쎅거림 등으로 판단하면 30프로정도는 misdiagnosis
복합적 질환으로서 gold standard가 존재하지 않는다.
이전에 symptom sign score를 만듦
그렇지만 약한 증상을 가진 사람들은 추가 진단에 의해 diagnosis해야함.
linear regression model을 사용해서 accuracy를 보니 symptom sign score만놓고 보면 70정도.
*equivocal: 모호한
*non-specific: 불특정의, 일반적인
*peripheral: 말초의, 중요하지 않은 부분의
2. Methods
classifier: logistic analysis, SVM and DNN
초기에 tensorflow로 변수 초기화하고, 뭐 딥러닝해서 해주는 파라미터 튜닝등을 거쳤다. 블라블라
(1) logistic regression analysis
(2) SVM
(3) DNN
10 fold-stratified cross validation
'논문 > 의료논문' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Novel Machine Learning Can Predict Acute Asthma Exacerbation 논문 리뷰 (0) | 2021.04.27 |
|---|---|
| 논문 abstract 간단 정리 - Omics 연구 영국 기관 논문 (0) | 2019.12.27 |
Clinical and inflammatory characteristics of the European U-BIOPRED adult severe asthma cohort
1. 연구 형태
다기관 전향적 연구, 환자들이 등록 이전에 최소 6개월의 follow-up이 있어야함.
2. cohort group
U-BIOPRED에서 정이한 severe asthma는 airtflow reversibility와 airway hyperresponsiveness 혹은 감소하는 것 FEV1 of 12% predicted, tapering maintenance treatment후 4주이내의 200ml감소. 4가지 그룹으로 모음
(1) Group A:12개월간 non-smoker with 5 pack-year smoking history, with asthma and uncontrolled sympoms odfineo occording to gina and frequemt exacerbations oespite high-dose inhaled corticosteroios.
(2) Group B: Group A랑 동일하나 현재 스모커나 ex-smoker
(3) Group C: non-smoker with mile/moderate asthmatics. controlled or partially controlled sympotms, whilst receiving a dose of <500 microgram fluticasone propionate/day or equivalent
(4) Group D: healthy non-smoking asthmatics. No history of asthma or wheeze, no chronic respiratory disease, nonsmoker for at least the past 12 months and their pre-bronchodilator FEV1 was >= 80% pred.
3. Protocal and assessment
대략 천식환자가 받아야할 테스트들에 대한 설명이 있음
4. statistical analysis
data는 평균이나 중앙값으로 요약되고 nonsymmetrical variable은 positive skew이거나 log-transformed되었다.
Missing value were not imputed. p=value는 general linear model이나 혹은 logidstic model로 계산되었다.
5. Result
6. spirometry
SAn/SA is lower than other groups in FEV1, FVC, FEV1/FVC
7. medication
SAn/SAs/ex is higher rate of medication than other groups.
8. atopy and comorbidity
There was a higher incidence atopy in the four groups.
9. Blood and sputum in biomarkers
blood eosinophil counts
blood neutrophil counts
10. Exhaled nitric oxide
FeNo
11. Discussion
'논문' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 시계열데이터 의료논문 요약 PPT (0) | 2022.10.13 |
|---|
논문 abstract 간단 정리 - Omics 연구 영국 기관 논문
1. Application of ’omics technologies to biomarker discovery in inflammatory lung diseases
- Craig E. Wheelock1,2, Victoria M. Goss 3, David Balgoma1
=> 오믹스 필드 내에 폐질환 biomarker를 연구하기 위해 사용가능한 기술들을 리뷰해놓은 논문
2. A computational framework for complex disease stratification from multiple large-scale datasets
- Bertrand De Meulder1*† , Diane Lefaudeux1†, Aruna T. Bansal2
=> 멀티 오믹스 데이터 베이스와 복잡한 질환간의 얽혀있는 관계를 밝히기 위한 데이터 베이스를 build up한 framework에 대한 논문
3. Pathway discovery using transcriptomic profiles in adult-onset sever asthma
- Pieter-Paul Hekking, MD,
=> 논문 abstract가 그림으로 표현...무슨말...
4. Asthma similarities across ProAR (Brazil) and U-BIOPRED (Europe) adult cohorts of contrasting locations, ethnicity and socioeconomic status
- Alvaro A. Cruza,*, John H. Rileyb, Aruna T. Bansalc, Eduardo V. Ponted
=> 민족성이나 환경에 따라 asthma가 어떻게 달라지는지 비교하는 논문
*cross-sectional analysis를 두 어른집단에 대해 수행
SA 집단 사이에서 나이, 몸무게, 이전에 smoker였떤 비율과 FEV1 pre-bronchodilator는 비슷하다.
*횡단 연구에서 종단 연구와 가장 도드라지게 큰 차이점은 횡단 연구는 specific point in time을 연구한다는 것이겠다.
마찬가지로 자주 사용되는 부분은 주로 아이들의 발달, 성장에 관한 것이다. 딱! 동시적인 시점에서 동일 기간에, 여러 변수에 대해 연구대상을 뽑은 다음에 특징을 측정하는 형식.
[출처] 영어 교육학/Second Language Acquisition - Longitudinal study,(종단 연구), Cross-Sectional study,analysis,research(횡단 연구)|작성자 부기온앤온
5. Characteristics and treatment regimens across ERS SHARP severe asthma registries
- Job J.M.H. van Bragt, Ian M. Adcock, Elisabeth H.D. Bel, Gert-Jan Braunstahl
=> 11개국의 악성 천식 registry를 모은 데이터의 cross-sectional retrospective analysis를 수행.
characteristics를 주로 봄.
유럽의 악성천식 환자들의 population은 일관되지만 clinical characteristics와 treatment를 바꾼다. 대게 현재 ERS/ATS 가이드라인을 따르는 양상은 아니다.
각 나라별 characteristics를 보기 좋음.
* ERS( European Resporatory Society)
* This is the first study in the ERS Severe
Heterogeneous Asthma Research collaboration, Patient-centred (SHARP)
6. Clinical and inflammatory characteristics of the European U-BIOPRED adult severe asthma cohort
- Dominick E. Shaw1,44, Ana R. Sousa2,44, Stephen J. Fowler3, Louise J. Fleming4, Graham Roberts5,6,7,
=> 시스템생물학을 이용해 천식질병의 매카니즘을 개선하고 이해하려는 목적을 가짐.
*시스템생물학은 특정 생명현상에 대해 문제를 정의하고, 문제에 관련된 생명체의 구성 요소(유전자, RNA, 단백질, 대사물질 등)들의 정량적 변화를 오믹스 분석을 통해 시스템 수준에서 측정하며, 변화를 보이는 요소들 간의 상호작용을 표현하는 네트워크 모델을 구축, 분석하여, 문제에 대한 답으로 네트워크 상의 주요 신호경로에 기반한 가설을 제시하고 이를 증명하는 학문이다.
*Unbiased Biomarkers for the Prediction of Respiratory Disease Outcomes (U-BIOPRED)
*biomarker란 어떤 현상(질병, 감염, 주위환경 노출 등)을 나타내는 존재의 유기체에서 측정 가능한 물질을 말한다.
7. Diagnosis and definition of severe refractory asthma: an international consensus statement from the Innovative Medicine Initiative (IMI)
- Elisabeth H Bel,1 Ana Sousa,2 Louise Fleming,3 Andrew Bush,4 K Fan Chung,5
=> severe refractory asthma에 대한 정의와 새로운 진단 가이드라인을 제시함.
8. ERS/EAACI statement on severe exacerbations in asthma in adults: facts, priorities and key research questions
- Arnaud Bourdin1, Leif Bjermer2, Christopher Brightling3, Guy G. Brusselle4
=> EAACI와 ERS가 severe exacerbation에 대한 명확한 정의와 그에 대한 research questions와 priorities를 분명히 정의하기 위해서 task force를 설립했다.
~ asthma에 대한 대략적인 임상정보를 보기 위한 논문으로 적절함.
9. Management of Severe Asthma: a European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society Guideline
-Fernando Holguin, Juan Carlos Cardet, Kian Fan Chung, Sarah Diver, Diogenes S. Ferreira
=> 위 8번 논문에 대한 대답
10. “T2-high” in severe asthma related to blood eosinophil, exhaled nitric oxide and serum periostin
- Stelios Pavlidis1,2, Kentaro Takahashi1,3, Francois Ng Kee Kwong1, Jiaxing Xie1
=> 현재 사용가능한 clinical biomarker로 AEC-defined T2-high phenotype을 U-BIOPRED cohort내에서 예측할 수 있는지 시험한다.
통계적인 기법을 이용해서 어떤 요소가 T2-high phenotype에 영향을 주는지 알아냄
~ 나중에 머신러닝을 이용해도 될 것 같은 논문
* higher exhaled nitric oxide fraction (FeNO, 호기산화질소검사)
- 기도의 염증상태 파악을 위해 호산구성 기관지 염증을 진단하고 스테로이드에 대한 치료 반응 예측 및 모니터링에 유용합니다.
11. Three Major Effors to Phenotype Asthma: Severe Asthma Research Program, Asthma Disease Endotyping for personalized Therapeutics, and Unbiased Biomarkers for the Prediction of Respiratory Disease Outcome
- Philip E. Silkoff, MD
=>
Unbiased Biomarkers for the prediction of respiratory disease outcome을 보기에 적절
논문들이 대체로 위와같은 내용을 지향함.
*표현형(phenotype)은 생명체의 관찰 가능한 특징적인 모습이나 성질을 의미한다. 눈 색깔이나 키와 같은 생김새뿐만 아니라 행동, 발생, 생리학적 또는 생화학적 특성 등 구별 가능한 다양한 생명현상을 포함한다. 이러한 표현형은 선천적으로 한 개체의 유전자형(genotype)에 의해 결정될 뿐 아니라, 후천적으로 다양한 환경인자에 의해서도 영향 받을 수 있다. 멘델의 유전연구에서 나타난 것처럼 대립이 되는 특정 표현형이 존재하기도 하는 반면, 여러 가지의 다양한 표현형이 존재하는 경우도 있다.
12. Treatable traits in the European U‐BIOPRED adult asthma cohorts
11번 논문과 비슷한 목적
13. U-BIOPRED: evalualtion of the value of a public-private partnership to industry
- John H. Riley, Veit J.Erpenbeck
=> U-BIOPRED는 IMI와 함게 시작을 한다. asthma에 대한 이해를 하기 위해 clinical과 multi-omics를 통합하여 접근하고 여러 산업과 아카데미 환자들의 통합을 통해 이를 이루어 가는 과정을 리뷰하는 논문이다.
14. Validated and longitudinally stable asthma phenotypes based on cluster analysis of the ADEPT study
- Matthew J. Loza1, Ratko Djukanovic2, Kian Fan Chung3
=>
*ADEPT (Airways Disease Endotyping for Personalized Therapeutics)
15. Moderate-to-severe asthma in individuals of European ancestry: a genome-wide association study
-Nick Shrine*, Michael A Portelli*, Catherine John*, María Soler Artigas, Neil Bennett, Robert Hall, Jon Lewis, Amanda P Henry
=> 2가지 stag로 case-control design을 수행
1. 환자군은 적절한 약물과 진단을 의사에게 받았을때, moderate-to-severe 환자들, 대조군은 이외의 천식, 알러지 등을 진단 받지 않은 환자들.
2. 독립적인 case and control 환자들을 수집
두 stage의 차이는 첫번째는 genome-wide sassociation study이고 두번쨰는 p가 1*10^-6보다 작은 임계선에 다다르게 하는 독립적인 variant를 follow up하는 것.
결론: 24개의 moderate-to-severe asthma와 관련있는 genome-wide significant signals를 찾아냄
16. Enhanced oxidative stress in smoking and exsmoking severe asthma in the U-BIOPRED cohort
- Rosalia EmmaID1, Aruna T. BansalID2, Johan Kolmert3,4, Craig E. Wheelock3, SwenErik Dahlen4
=> severe asthma U-BIOTRED subjects들에서 smoker들과 ex-smoker and non-smoker들로 나눠, clinical data, urine and sputum을 얻어낸다.
17. Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds as Markers for Medication Use in Asthma
- Paul Brinkman, Waqar M. Ahmed, Cristina Gómez, Hugo H. Knobel, Hans Weda (읽기 쉬울듯)
=> 몸의 화학물의 변화를 반영하는 volatile organic compounds를 포함한 exhaled breath정보를 U-BIOPRED cohort로부터 추출한다.
exhaled VOCs의 연관성을 분석하는것이 목표이다.
baseline과 baseline에서 12-18개월의 팔로우업을 수행한 sample을 수집한다.
univariate과 multivariate modeling을 사용해 AUROC를 볼 것이다. (regression analysis)
18. Identification and prospective stability of electronic nose-derived inflammatory phenotypes in patients with severe asthma (clustering 연구에 도움이 될 것 같은 연구논문)
- Paul Brinkman, MSc
19. Lipid phenotyping of lung epithelial lining fluid in healthy human volunteers
- Joost Brandsma1 · Victoria M. Goss1 · Xian Yang2 · Per S. Bakke3 · Massimo Caruso4 · Pascal Chanez5
=> 건강한 성인의 lipdome을 특정짓고, ELF lipid phenotypes와 demographics사이의 관련성을 시험한다.
TDA는 비교할만한 sputum lipidomes를 가진 객체들을 그룹화하기 위해 사용됐다.
20. Metabolomics analysis identifies different metabotypes of asthma severity
- Stacey N. Reinke1, Héctor Gallart-Ayala1, Cristina Gómez1,2, Antonio Checa1,2
'논문 > 의료논문' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Novel Machine Learning Can Predict Acute Asthma Exacerbation 논문 리뷰 (0) | 2021.04.27 |
|---|---|
| 천식 머신러닝 논문 리뷰 - Deep learning facilitates the diagnosis of adult asthma, Katsuyuki Tomita (0) | 2020.03.16 |